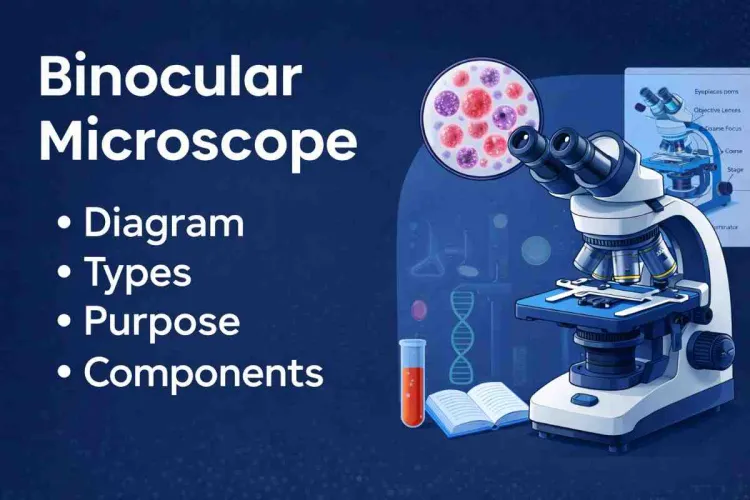
What is Binocular Microscope
A binocular microscope is a powerful device used to enlarge small objects for detailed observation. Unlike conventional microscopes with a single eyepiece, it features two eyepieces that improve viewing comfort and reduce eye strain. The microscope creates separate optical paths for each eye, providing a three-dimensional view of the specimen. Because of this, binocular microscopes are widely used in education, medical diagnosis, and scientific research. They are available in various models with different magnification levels and features.
Purpose of a Binocular Microscope
A binocular microscope is a microscope used to view microscopic objects in a clear manner with the help of magnification. It is implemented at schools, research laboratories, hospitals, and industrial quality control departments. It enables people to examine cells, bacteria, tissues, and other substances that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Binocular microscopes are used as compared to monocular microscopes since both eyes are utilised. This forms a more natural and relaxing viewing position.
A Binocular Microscope's Diagram

Here is the Parts of Binocular Microscope
1. Eyepieces (Ocular Lenses)—Two glasses that enlarge the picture, normally 10x or 15x.
2. Objective Lenses—This type of lens can be replaced with an alternate lens that has a different magnification, e.g. a 4x, 10x, 40x or 100x lens.
3. Light Source—An in-built LED or halogen lamp that bends the light up through the specimen.
4. Condenser and Diaphragm—They regulate the intensity of the light and focus on the sample to have a clear view.
5. Focusing Knobs—Coarse and fine knobs are used to move the stage to sharpen the image.
6. Arm and Base—Help to hold the frame and bring about stability when in use.
Working of a Binocular Microscope
The light is directed to the specimen and onto the objective lens. The picture is enlarged and reflected through the prisms within the head. The eyepieces had the prisms dividing the image into two optical paths. This enables both eyes to see the same picture at slightly different angles. The outcome is a three-dimensional view, which enhances clarity.
Types of binocular microscopes
1. Coupled Binocular Microscope
Applied to thin and transparent specimens like cells or bacteria. It is more magnified, usually to 1000x.
2. Stereoscopic Binocular Microscope
Applied to larger and opaque items such as insects, plants and small machine components. It produces a 3D picture of lower magnification of typically 10x-80x.
3. The Digital Binocular Microscope
Brings together optical lenses and a digital camera. The picture is displayed on the screen and this assists in teaching or recording.
The difference between a Binocular Microscope and other Microscopes
The major difference of a binocular microscope with other microscopes is in the viewing system. It possesses two eyepieces rather than one. This renders the whole process of watching to be less straining to your eyes. There is also a monocular microscope which has a single eyepiece.
It is also easy and frequently applied in schools for studying. A trinocular microscope provides an additional port for a camera that is used in research and taking images. Microscopes. Binocular microscopes have increased depth perception compared to monocular types. They also decrease fatigue in intensive scrutiny. A binocular model would be the sensible one in case you require comfort and precision in watching.
Benefits of the Binocular Microscopes
- Less strain on the eyes during study hours
- Less painful position and concentration.
- Better depth perception
- Adequate to test samples in details.
- Applicable in education, as well as research
Binocular microscopes are found in many applications
- Education -Students are taught biology and material science.
- Medical Laboratories -These are used in analyzing blood, tissues and microorganisms.
- Research Centers- Helpful in the study of cell structures and chemical reactions.
- Industrial Inspection- Applied to electronics, metallurgy and high precision manufacturing.
Maintenance Tips
Never use your hands to clean lenses. Clean them using lens paper/ microfiber cloth.
- Cover the microscope with a lens.
- Store in a dry, dust-free area.
- Switch off the source of light when not in use.
- Check mechanical parts on the regular basis to ensure free movements.
- The thing is how to select the correct Binocular Microscope.
Purpose Select a compound model to use in biology or a stereo model to use in inspection work
- Magnification - Choose lenses according to the amount of detail required.
- Lighting- LED is economical and less hot in comparison with halogen.
- Base Stability and Smoothness of Focus: Check.
- Adjustment without difficulty—interpupillary distance and diopter adjustments enhance comfort.
Final Thoughts
A binocular microscope is a convenient tool to any person in science or education. It is also more comfortable, accurate and more precise with images compared to single eye piece models. You save time by understanding how it works and preserving it in the right way, you will prolong its lifetime and achieve the same result in your studies or experiments.
FAQs about Binocular Microscopes
1. What does a binocular microscope mean?
A binocular microscope refers to a two-eyed microscope that has two eyepieces and provides the user with a view of the specimen through both eyes. This kind of viewing is considered to be more relaxing, and it is less likely to cause the observer's eye to get tired when compared to the case of a monocular (one-eyepiece) microscope.
2. What are the reasons for using a binocular microscope?
This instrument's primary objective is to render the invisible microscopic objects to the naked eye by magnifying them greatly. It finds its application in schools, research laboratories, hospitals, and even industries where the study of cells, tissues, bacteria, and small structures is involved, making them visible through the microscope.
3. In what ways is a binocular microscope superior to a monocular microscope?
The advantages of binocular microscopes: Usage of both eyes creates a more natural viewing experience Less eye fatigue from the use of both eyes Better perception of depth More convenience on the part of the user during long sessions of observations
4. What are the main parts of the binocular microscope?
The main components of the microscope are: Eyepieces (ocular lenses) - usually of 10x or 15x magnification Objective lenses - cover the range of 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x and can be changed Light source - It can be either LED or halogen. Condenser and diaphragm - to regulate the focus and the intensity of light Focusing knobs -- coarse and fine adjustment Arm and base - to give support
5. What is the working principle of a binocular microscope?
The light goes through the sample to the objective lenses that magnify the image. Inside the head of the microscope, some prisms divide the image into two optical paths, and one eye sees the sample from one angle while the other eye sees it from a slightly different angle, creating the impression of 3D.

